Net Zero: The Ultimate Guide
What does net zero mean?
The effects of Global Warming, such as rising sea levels and intense droughts, will be catastrophic to the health of our planet and the human race. The Paris Climate Agreement demanded a shift in the global attitude towards Climate Change. The treaty addressed the importance of reducing and achieving Net Zero Greenhouse Gas emissions to limit the threat of global warming.
The term Net-Zero has since been considered critical in combating climate change. Since the treaty was signed in 2015, the government and many organisations have established Net Zero targets. The UK has committed to achieving a 78% reduction in emissions by 2035, working towards Net Zero by 2050 – and many other organisations have followed suit.
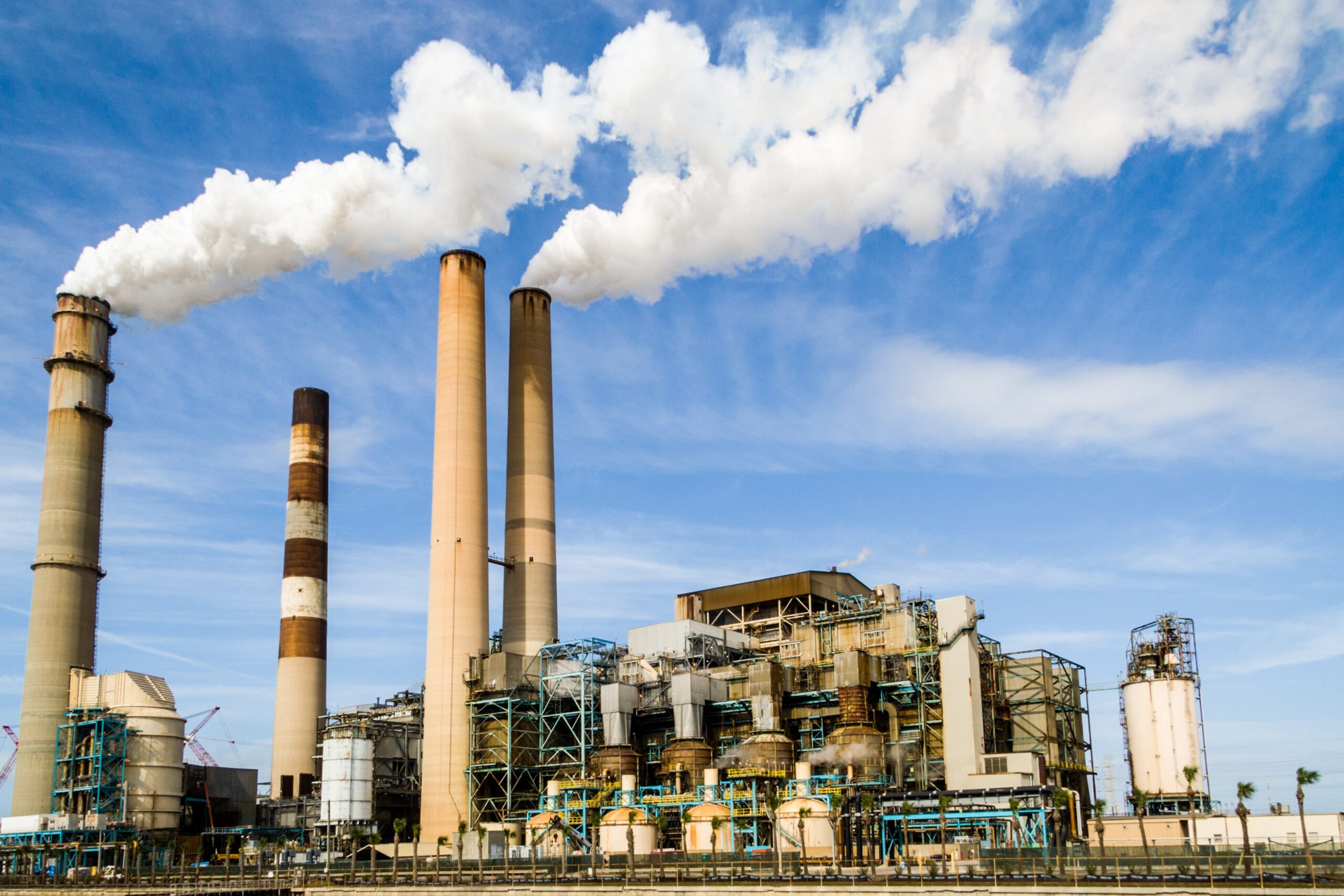

What is net zero carbon?
Although committing to Net Zero is a growing trend, understanding what it means in practice is often ambiguous. To put it simply, Net-Zero involves reducing Greenhouse Gas emissions in activities as much as possible, followed by supporting the removal of Carbon Dioxide produced by any emissions the business cannot remove.
Are you still confused? As a simplified example, an organisation could achieve Net Zero by first identifying and undertaking changes across the business to reduce emissions by implementing green technologies, e.g., installing solar panels to generate off-grid electricity.
Any emissions that cannot be reduced will be offset by investing in climate-friendly initiatives, e.g., tree planting. To achieve the UK’s Net-Zero by 2050 target, the government will phase out coal and gas power and generate electricity through renewables and nuclear power. The government is investing heavily in carbon capture technologies, a likely solution designed to prevent the release of carbon into the atmosphere.
Sign the pledge today!
Net zero vs carbon neutral
The term Net Zero is often used interchangeably with Carbon Neutrality, although they are fundamentally different. As previously discussed, Net Zero involves undertaking actions to reduce carbon emissions, followed by offsetting any carbon which cannot be removed. Carbon Neutrality defines the balancing of Greenhouse Gas emissions through offsetting an equivalent amount of carbon to the amount produced.
How to become carbon neutral
The notion of Carbon Neutrality is widely criticised for lacking commitment to reducing emissions before undertaking offsetting activities. Relying solely on offsetting is problematic; it fails to address the overarching issue of carbon entering the atmosphere—Furthermore, the lack of regulation in offsetting results in poor standards and bad practices. Offsetting activities can seem attractive for organisations as the prices are low, allowing them to claim to be climate-conscious. However, cheap, substandard offsetting activities often fail to offset the amount of pollution they are meant to; efforts are quickly reversed or are immeasurable.
What is the biggest contributor to global warming?
Carbon dioxide is derived from both human and natural sources. Carbon dioxide is an important Greenhouse Gas as it enables heat to be trapped in the earth’s atmosphere, which would be inhospitably cold without. However, the immense level of Co2 that human activity emits is at a record high and is threatening the health and wellbeing of the planet and people. Dangerous levels of carbon in the atmosphere result in poor air quality, which can cause respiratory diseases. The increasing temperature causes extreme weather, resulting in food shortages, increasing wildfires, melting icecaps, threats to biodiversity.
What produces the most CO2 on Earth?
The burning of fossil fuels for electricity and heat generation is the leading emitter of Co2 in the world. Society has grown increasingly concerned about the effects of climate change and global warming. Technologies that generate electricity and heat from renewable sources have begun to take precedence over non-renewables, with coal usage almost obsolete in the UK.
Get to know more about Net Zero
At Climate Change Professionals, we provide expert training which can allow anyone to become more knowledgeable about Net Zero and climate change.
Get involved and take your first steps to becoming a Climate Change Professional and make your pledge today.
Copyright © 2021 Climate Change Professionals